1 南京大学 产业技术研究苏州总院, 江苏 苏州 215000
2 南京大学 金陵学院, 南京 210094
3 上海航天电子技术研究所, 上海 201109
4 上海航天控制技术研究所, 上海 201109
光敏晶体管是空间飞行器光电编码器中的重要组成部分, 对空间高能质子引起的位移损伤效应较为敏感。文章通过试验获得了光敏管的核心参数输出电流与质子能量、位移损伤剂量、工作状态、屏蔽材料的关系。在50、60、70、92 MeV四种能量的质子辐照下, 器件输出电流及光电转换效率最大下降80%。晶体管内部光敏二极管初始光电流的下降和晶体管电流增益的下降共同作用造成了输出电流随位移损伤剂量的增加不断衰减。不锈钢和三明治屏蔽结构对60 MeV能量质子几乎没有遮挡效果。通过提高输入光照强度, 增大初始光电流, 可以降低位移损伤效应的影响。另外, 采用PIN型光电二极管, 增大耗尽区面积, 也是可行的加固方法之一。
光敏晶体管 高能质子 位移损伤效应 非电离能损 phototransistor high energy proton displacement damage effect non-ionizing energy loss
光子学报
2022, 51(11): 1109001
1 西安工业大学光电工程学院陕西省薄膜技术与光学检测重点实验室,陕西 西安 710021
2 中国兵器科学院宁波分院,浙江 宁波 310022
数字全息测量系统中,记录过程引入的散斑噪声严重影响全息图质量,导致三维重建结果存在误差。相位提取是数字全息三维测量系统中影响精度的关键技术,而相位解包是获得正确连续相位的关键环节。为了抑制数字全息测量系统中的散斑噪声,提出了一种处理包裹相位的散斑噪声抑制方法。首先应用二维高斯窗口在频域内对包裹相位进行局部分析,并基于窗口傅里叶基函数与包裹相位的高相关性选取阈值;然后根据阈值舍弃噪声频谱,获得低散斑噪声的包裹相位。以微透镜阵列为测试对象,实现了数字全息测量系统中散斑噪声的有效抑制。实验结果表明,所提方法保留了包裹相位的跳变边界,有效提高了数字全息测量系统的三维重建精度,与未去噪的结果相比,残差降低了28.35%(峰谷值)和20.23%(均方根)。
全息 数字全息 散斑噪声 二维高斯窗口 包裹相位 三维重建 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(16): 1609002
1 中国科学技术大学 中国科学院量子信息重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230026
2 中国科学技术大学 中国科学院量子信息和量子物理协同创新中心,安徽 合肥 230026
具有高品质因子(Q 值)的光学谐振腔能够长时间将光束缚在较小的模式体积内,极大地增强了光与物质的相互作用,成为集成光学器件中具有重大潜力的重要组成部分。聚焦于目前广泛应用于集成非线性光学领域的氮化硅材料平台,为了解决大尺寸氮化硅微环腔由拼接误差、表面粗糙等因素导致的散射损耗较大的问题,进行了一系列的工艺改进以提高大尺寸氮化硅微环腔的品质因子。结果表明:通过薄膜再沉积工艺可以有效降低氮化硅波导的散射损耗,半径为560 μm的大尺寸氮化硅微环腔的本征Q值得到了平均26% 的提升。得益于提高的微腔Q 值,在氮化硅微环腔中实现了重复频率40 GHz 的光学频率梳。
氮化硅微环腔 品质因子 光学频率梳 silicon nitride microring resonator quality factor optical frequency comb 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(5): 20220302

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center For Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Center for Micro and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication, University of Science and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
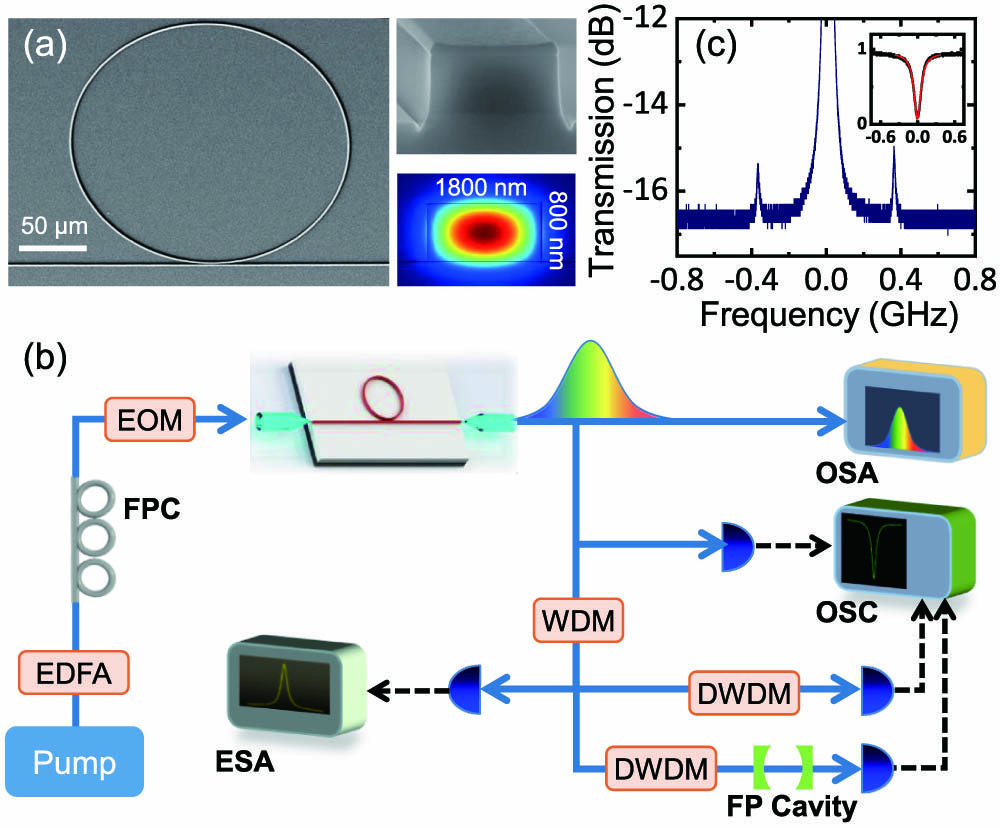
The microresonator-based soliton microcomb has shown a promising future in many applications. In this work, we report the fabrication of high quality (Q) microring resonators for soliton microcomb generation. By developing the fabrication process with crack isolation trenches and annealing, we can deposit thick stoichiometric film of 800 nm without cracks in the central area. The highest intrinsic Q of the microring obtained in our experiments is about , corresponding to a propagation loss as low as 0.058 dBm/cm. With such a high Q film, we fabricate microrings with the anomalous dispersion and demonstrate the generation of soliton microcombs with 100 mW on-chip pump power, with an optical parametric oscillation threshold of only 13.4 mW. Our integrated chip provides an ideal platform for researches and applications of nonlinear photonics and integrated photonics.
silicon nitride microresonator optical frequency comb dissipative Kerr soliton Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(3): 032201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Center for Micro and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication, University of Science and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
4 e-mail: clzou321@ustc.edu.cn
Dissipative Kerr solitons offer broadband coherent and low-noise frequency combs and stable temporal pulse trains, having shown great potential applications in spectroscopy, communications, and metrology. Breathing solitons are a particular kind of dissipative Kerr soliton in which the pulse duration and peak intensity show periodic oscillation. Here we have investigated the breathing dissipative Kerr solitons in silicon nitride () microrings, while the breathing period shows uncertainties of around megahertz (MHz) order in both simulation and experiments. This instability is the main obstacle for future applications. By applying a modulated signal to the pump laser, the breathing frequency can be injection locked to the modulation frequency and tuned over tens of MHz with frequency noise significantly suppressed. Our demonstration offers an alternative knob for the control of soliton dynamics in microresonators and paves a new avenue towards practical applications of breathing solitons.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(8): 08001342

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
2 College of Information Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
3 Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
The dissipative sensing based on a self-interference microring resonator composed of a microring resonator and a U-shaped feedback waveguide is demonstrated experimentally. Instead of a frequency shift induced by the phase shift of the waveguide or the microcavity, the dissipative sensing converts the phase shift to the effective external coupling rate, which leads to the change of linewidth of the optical resonance and the extinction ratio in the transmission spectrum. In our experiment, the power dissipated from a microheater on the feedback waveguide is detected by the dissipative sensing mechanism, and the sensitivity of our device can achieve 0.22 dB/mW. This dissipative sensing mechanism provides another promising candidate for microcavity sensing applications.
Integrated optics devices Resonators Optical sensing and sensors Photonics Research
2018, 6(7): 07000681





